Hello and welcome! 🌟 Ready to create a YouTube clone that’s rock-solid and feature-rich? 🔒

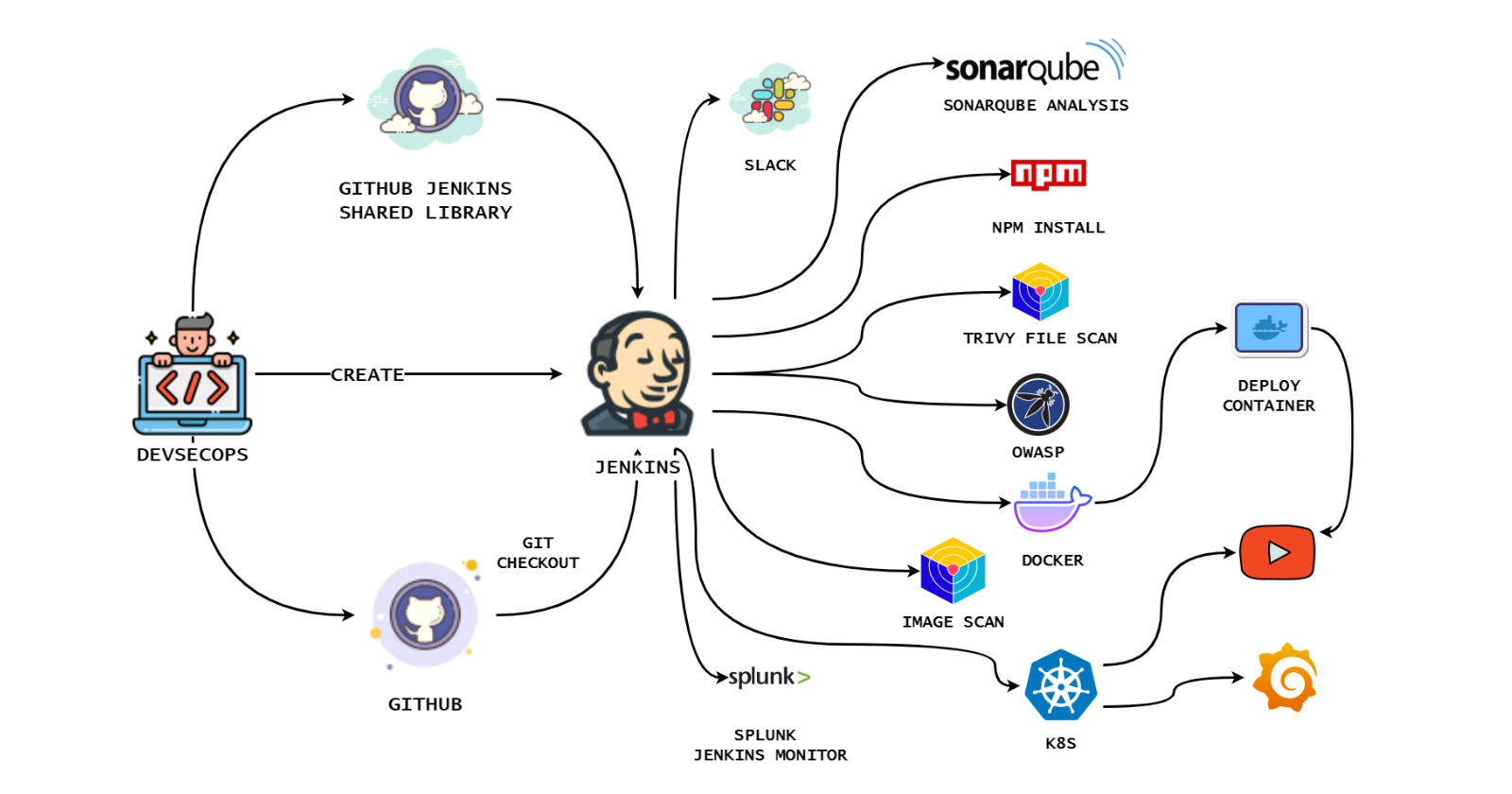
This blog is your gateway to a secure DevSecOps pipeline for your project. With Kubernetes, Docker, SonarQube, Trivy, OWASP Dependency Check, Prometheus, Grafana, Jenkins (and a shared library), Splunk, Rapid API, Slack notifications, and efficient parameters for creating and destroying your environment, we’ve got you covered.
Let’s build a YouTube clone that’s not just cutting-edge but also protected. Join us on this journey! 💪📽️
Github Repo: https://github.com/Aj7Ay/Youtube-clone-app.git
video on youtube: https://youtu.be/OCZriuQe08U?si=INELPohlN-FZK-r6
Normal Jenkinsfile you can use this one without the shared library
def COLOR_MAP = [
'FAILURE' : 'danger',
'SUCCESS' : 'good'
]
pipeline{
agent any
tools{
jdk 'jdk17'
nodejs 'node16'
}
environment {
SCANNER_HOME=tool 'sonar-scanner'
}
stages {
stage('clean workspace'){
steps{
cleanWs()
}
}
stage('Checkout from Git'){
steps{
git branch: 'main', url: 'https://github.com/Aj7Ay/Youtube-clone-app.git'
}
}
stage("Sonarqube Analysis "){
steps{
withSonarQubeEnv('sonar-server') {
sh ''' $SCANNER_HOME/bin/sonar-scanner -Dsonar.projectName=youtube \
-Dsonar.projectKey=youtube '''
}
}
}
stage("quality gate"){
steps {
script {
waitForQualityGate abortPipeline: false, credentialsId: 'Sonar-token'
}
}
}
stage('Install Dependencies') {
steps {
sh "npm install"
}
}
stage('OWASP FS SCAN') {
steps {
dependencyCheck additionalArguments: '--scan ./ --disableYarnAudit --disableNodeAudit', odcInstallation: 'DP-Check'
dependencyCheckPublisher pattern: '**/dependency-check-report.xml'
}
}
stage('TRIVY FS SCAN') {
steps {
sh "trivy fs . > trivyfs.txt"
}
}
stage("Docker Build & Push"){
steps{
script{
withDockerRegistry(credentialsId: 'docker', toolName: 'docker'){
sh "docker build --build-arg REACT_APP_RAPID_API_KEY=f0ead79813ms -t youtube ."
sh "docker tag youtube sevenajay/youtube:latest "
sh "docker push sevenajay/youtube:latest "
}
}
}
}
stage("TRIVY"){
steps{
sh "trivy image sevenajay/youtube:latest > trivyimage.txt"
}
}
stage('Deploy to container'){
steps{
sh 'docker run -d --name youtube1 -p 3000:3000 sevenajay/youtube:latest'
}
}
stage('Deploy to kubernets'){
steps{
script{
withKubeConfig(caCertificate: '', clusterName: '', contextName: '', credentialsId: 'k8s', namespace: '', restrictKubeConfigAccess: false, serverUrl: '') {
sh 'kubectl apply -f deployment.yml'
}
}
}
}
}
post {
always {
echo 'Slack Notifications'
slackSend (
channel: '#channel name', #change your channel name
color: COLOR_MAP[currentBuild.currentResult],
message: "*${currentBuild.currentResult}:* Job ${env.JOB_NAME} \n build ${env.BUILD_NUMBER} \n More info at: ${env.BUILD_URL}"
)
}
}
}STEPS:
Step 1: Launch an Ubuntu 22.04 instance for Jenkins
Log into AWS Console: Sign in to your AWS account.
Launch an Instance:
Choose “EC2” from services. Click “Launch Instance.”
Choose an AMI: Select an Ubuntu image.
Choose an Instance Type: Pick “t2.large.”
Key Pair: Choose an existing key pair or create a new one.
Configure Security Group:
Create a new security group. Add rules for HTTP, and HTTPS, and open all ports for learning purposes. Add Storage: Allocate at least 20 GB of storage.
Launch Instance: Review and launch the instance.
Access Your Instance: Use SSH to connect to your instance with the private key.
Keep in mind, that opening all ports is not recommended for production environments; it’s just for educational purposes.

Connect to Your EC2 Instance and Install Jenkins:
Use MobaXterm or PuTTY to connect to your EC2 instance. Create a shell script named
sudo vi install_jenkins.shPaste the following script:
#!/bin/bash
sudo apt update -y
wget -O - https://packages.adoptium.net/artifactory/api/gpg/key/public | tee /etc/apt/keyrings/adoptium.asc
echo "deb [signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/adoptium.asc] https://packages.adoptium.net/artifactory/deb $(awk -F= '/^VERSION_CODENAME/{print$2}' /etc/os-release) main" | tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/adoptium.list
sudo apt update -y
sudo apt install temurin-17-jdk -y
/usr/bin/java --version
curl -fsSL https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable/jenkins.io-2023.key | sudo tee /usr/share/keyrings/jenkins-keyring.asc > /dev/null
echo deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/jenkins-keyring.asc] https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable binary/ | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/jenkins.list > /dev/null
sudo apt-get update -y
sudo apt-get install jenkins -y
sudo systemctl start jenkins
sudo systemctl status jenkinsSave and exit the text editor.
Make the script executable:
sudo chmod +x install_jenkins.shRun the script:
./install_jenkins.shThe script will install Jenkins and start the Jenkins service.
You will need to go to your AWS EC2 Security Group and open Inbound Port 8080 since Jenkins works on Port 8080.
Now, grab your Public IP Address
EC2 Public IP Address:8080
sudo cat /var/lib/jenkins/secrets/initialAdminPassword

Now, install the suggested plugins.

Jenkins will now get installed and install all the libraries.
Create an admin user

Click on save and continue.
Jenkins Dashboard

Step2A: Install Docker on the Jenkins machine
Run the below commands to install the docker
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install docker.io -y
sudo usermod -aG docker $USER #my case is ubuntu
newgrp docker
sudo chmod 777 /var/run/docker.sockAfter the docker installation, we will create a Sonarqube container (Remember to add 9000 ports in the security group).
Run this command on your EC2 instance to create a SonarQube container:
docker run -d --name sonar -p 9000:9000 sonarqube:lts-community

Now copy the IP address of the ec2 instance
ec2-public-ip:9000
Enter username and password, click on login and change password
username admin
password admin
Update New password, This is Sonar Dashboard.

Step2B: Install Trivy on Jenkins machine
Create a shell script
sudo vi trivy.shPaste the below commands
sudo apt-get install wget apt-transport-https gnupg lsb-release -y
wget -qO - https://aquasecurity.github.io/trivy-repo/deb/public.key | gpg --dearmor | sudo tee /usr/share/keyrings/trivy.gpg > /dev/null
echo "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/trivy.gpg] https://aquasecurity.github.io/trivy-repo/deb $(lsb_release -sc) main" | sudo tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list.d/trivy.list
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install trivy -yProvide executable permissions and run the shell script
sudo chmod +x trivy.sh
./trivy.shThis will install Trivy on our Jenkins machine.
Step3A: Launch an Ubuntu instance for Splunk
Step 1: Launch Instances
- Log in to your AWS console or your chosen cloud provider.
- Navigate to the EC2 service and launch Ubuntu 22.04 instances. Ensure you select T2.medium as the instance type and allocate 24GB of storage to each instance.
Step 2: Install Splunk
At this point, the first machine is set up with Jenkins. You can now move to the second machine and proceed with the installation of Splunk.
Connect to your second instance using Putty or Mobaxtreme.To download and install Splunk on your Ubuntu instance use the wget command, use the following command:
wget -O splunk-9.1.1-64e843ea36b1-linux-2.6-amd64.deb "https://download.splunk.com/products/splunk/releases/9.1.1/linux/splunk-9.1.1-64e843ea36b1-linux-2.6-amd64.deb"To Depackage the Splunk use the below command
sudo dpkg -i splunk-9.1.1-64e843ea36b1-linux-2.6-amd64.deb
sudo /opt/splunk/bin/splunk enable boot-startBy running this command, you ensure that Splunk Enterprise is configured to start automatically when your Ubuntu system boots, allowing you to seamlessly integrate it into your workflow.
Please note that after running this command, you should follow the on-screen prompts to accept the terms and complete the setup to 100%.

After completing the initial setup and accepting the terms, you’ll be prompted to create an admin user.
Administrator Username: Choose a username for the admin account. This should be a unique and secure username.
Administrator Password: Set a strong and secure password for the admin account. It’s important to choose a password that combines upper and lower-case letters, numbers, and special characters for enhanced security.
Confirm your password to ensure it matches the one you initially entered.
By creating an administrator username and password, you’ll have full access to your Splunk instance, allowing you to configure and manage it effectively.

The command sudo ufw allow OpenSSH is used to allow incoming SSH traffic through the UFW (Uncomplicated Firewall) on your Ubuntu system. It’s essential for enabling SSH access to your server.
sudo ufw allow openSSHBy running this command, you ensure that SSH access is permitted through your firewall, which is crucial for remote server management and administration.

The command sudo ufw allow 8000 is used to allow incoming network traffic on port 8000 through the UFW (Uncomplicated Firewall) on your Ubuntu system. It permits access to a specific port for network services or applications.
sudo ufw allow 8000
sudo ufw status: This command allows you to check the status of your UFW firewall. It will display information about whether the firewall is active, which rules are enabled, and whether it’s set to allow or deny specific types of traffic.
sudo ufw enable: This command is used to enable the UFW firewall if it’s not already active. Enabling the firewall ensures that the rules you’ve configured or will configure are enforced.
By running these commands, you can both check the current status of your firewall and activate it to apply the defined rules and settings.
sudo ufw status
sudo ufw enable
The command sudo /opt/splunk/bin/splunk start is used to start the Splunk Enterprise application on your system. When you run this command with superuser privileges (using sudo), it initiates the Splunk service, allowing you to begin using the Splunk platform for data analysis, monitoring, and other data-related tasks.
sudo /opt/splunk/bin/splunk start

After successfully starting your Splunk instance, you can now access its web interface to start exploring and analyzing your data.
Copy Your Splunk Instance Public IP Address: Navigate to your cloud provider’s console and find the public IP address of your Splunk instance.
Log in with Your Credentials: You’ll be prompted to log in with the administrator username and password you created during the setup process (typically using the command sudo /opt/splunk/bin/splunk enable boot-start).
splunk-public-ip:8000
This is the Splunk Dashboard

Step3B: Install the Splunk app for Jenkins
In Splunk Dashboard
Click on Apps –> Find more apps

Search for Jenkins in the Search bar
You will get the Splunk app for Jenkins and click on install

You will be prompted to provide your Splunk credentials. That’s why we created a Splunk account

Click on Agree and install
Now click on Go home

On the homepage of Splunk, you will see Jenkins has been added

In the Splunk web interface, go to Settings > Data Inputs.

Click on HTTP Event Collector.

Click on Global Settings

Set All tokens to enabled
Uncheck SSL enable
Use 8088 port and click on save

Now click on New token

Provide a Name and click on the next

Click Review
Click Submit

Click Start searching

Now let’s copy our token again
In the Splunk web interface, go to Settings > Data Inputs.

Click on the HTTP event collector

Now copy your token and keep it safe

Add Splunk Plugin in Jenkins
Go to Jenkins dashboard
Click on Manage Jenkins –> Plugins –> Available plugins
Search for Splunk and install it.

Again Click on Manage Jenkins –> System
Search for Splunk
Check to enable
HTTP input host as SPLUNK PUBLIC IP
HTTP token that you generated in Splunk
Jenkins IP and apply.

Now go to Putty or Mobaxtreme and In Splunk machine run this command
sudo ufw allow 8088
Now in the Jenkins dashboard Under Splunk click on Test connection

Restart Both Splunk and Jenkins
Let’s Restart our Splunk machine
Click on Settings –> Server controls

Restart and log in again

Now restart Jenkins and log in again.
<jenkins-ip:8080/restart> #this will restart jenkinsNow go to Splunk and click on the Jenkins app and you will get this output monitoring
Sample image.


Step4A: Integrate Slack for Notifications
Create a Slack account and create a channel Named Jenkins

Step4B: Install the Jenkins CI app on Slack
Go to Slack and click on your name
Select Settings and Administration
Click on Manage apps

It will open a new tab
Search for Jenkins CI and click on it

It will open another tab
Click on Add to Slack

Now choose your Slack channel
Click on Add Jenkins CI integration.

You will be redirected to this page

Copy the team subdomain and integration token credential ID for later use.


Install Slack Notification Plugin in Jenkins
Go to Jenkins Dashboard
Click on manage Jenkins –> Plugins –> Available plugins
Search for Slack Notification and install

Click on Manage Jenkins –> Credentials –> Global
Select kind as Secret Text
At Secret Section Provide Your Slack integration token credential ID
Id and description are optional and create
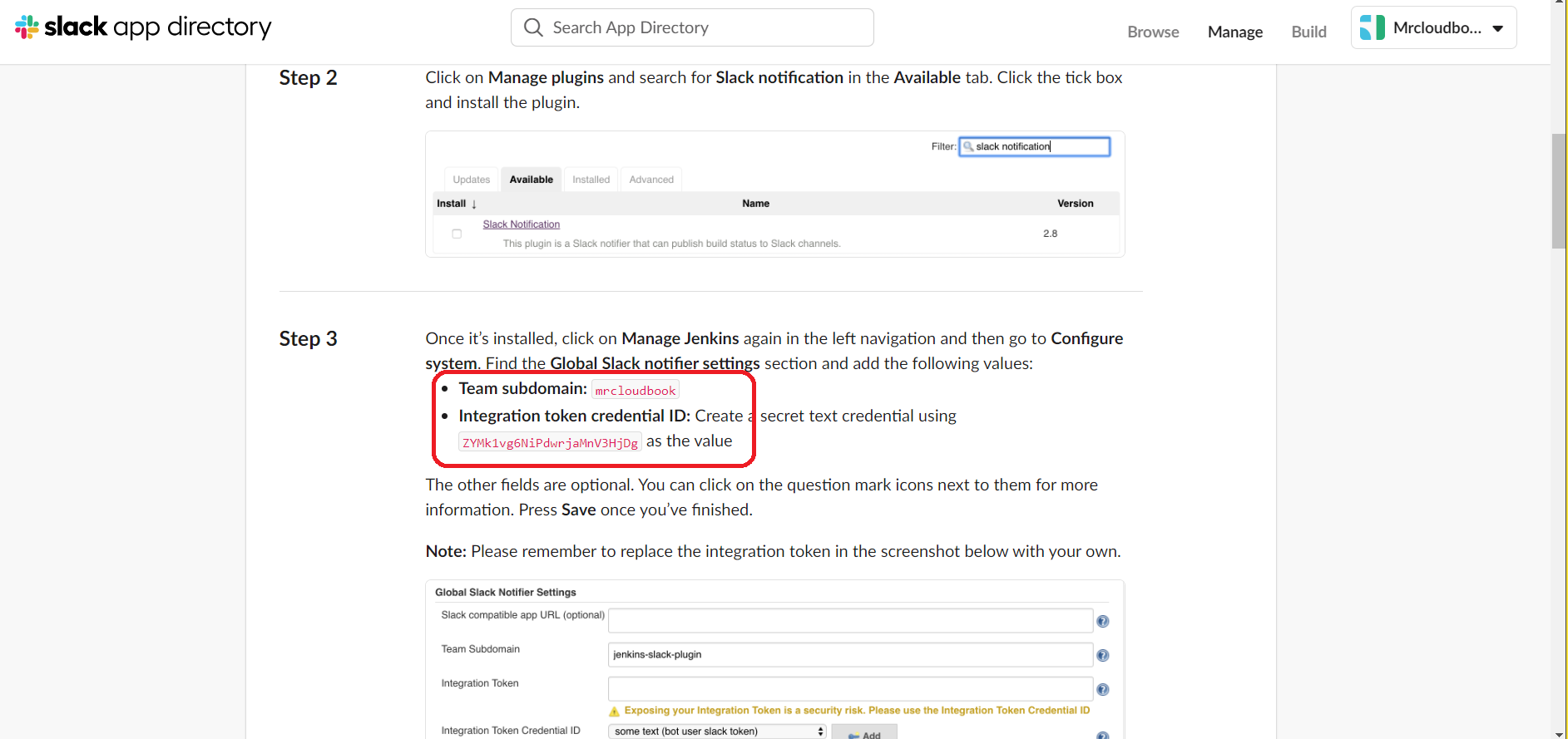

Click on Manage Jenkins –> System
Go to the end of the page
Workspace –> team subdomain
Credential –> Select your Credential for Slack
Default channel –> Provide your Channel name
Test connection


Click on Apply and save
Add this to the pipeline
def COLOR_MAP = [
'FAILURE' : 'danger',
'SUCCESS' : 'good'
]
post {
always {
echo 'Slack Notifications'
slackSend (
channel: '#channel name', #change your channel name
color: COLOR_MAP[currentBuild.currentResult],
message: "*${currentBuild.currentResult}:* Job ${env.JOB_NAME} \n build ${env.BUILD_NUMBER} \n More info at: ${env.BUILD_URL}"
)
}
}You will get a Notification in Slack
Step5A: Start Job
Go to Jenkins dashboard and click on New Item.
Provide a name for the Job & click on Pipeline and click on OK.
Create a new repository in GitHub named Jenkins_shared_library.

Connect to your VS Code
Create a directory named Jenkins_shared_library
Create a Vars directory inside it

Open Terminal
Run the below commands to push to GitHub
echo "# Jenkins_shared_library" >> README.md
git init
git add README.md
git commit -m "first commit"
git branch -M main
# make sure to change your repo Url here
git remote add origin https://github.com/Aj7Ay/Jenkins_shared_library.git
git push -u origin mainNow, Let’s Write a Groovy script for our Pipeline
Create a cleanWorkspace.groovy file and add the below code
#cleanWorkspace.groovy //cleans workspace
def call() {
cleanWs()
}Create checkoutGit.groovy file and add the below code
def call(String gitUrl, String gitBranch) {
checkout([
$class: 'GitSCM',
branches: [[name: gitBranch]],
userRemoteConfigs: [[url: gitUrl]]
])
}Now push them to GitHub using the below commands from vs code
git add .
git commit -m "message"
git push origin mainGo to Jenkins Dashboard
Click on Manage Jenkins –> system
Search for Global Pipeline Libraries and click on Add

Now Provide a name that we have to call in our pipeline


Click apply and save
Step5D: Run Pipeline
Go to Jenkins Dashboard again & select the job and add the below pipeline
@Library('Jenkins_shared_library') _ #name used in jenkins system for library
def COLOR_MAP = [
'FAILURE' : 'danger',
'SUCCESS' : 'good'
]
pipeline{
agent any
parameters {
choice(name: 'action', choices: 'create\ndelete', description: 'Select create or destroy.')
}
stages{
stage('clean workspace'){
steps{
cleanWorkspace()
}
}
stage('checkout from Git'){
steps{
checkoutGit('https://github.com/Aj7Ay/Youtube-clone-app.git', 'main')
}
}
}
post {
always {
echo 'Slack Notifications'
slackSend (
channel: '#channel name', #change your channel name
color: COLOR_MAP[currentBuild.currentResult],
message: "*${currentBuild.currentResult}:* Job ${env.JOB_NAME} \n build ${env.BUILD_NUMBER} \n More info at: ${env.BUILD_URL}"
)
}
}
}Build with parameters and build
Stage view

Step6: Install Plugins like JDK, Sonarqube Scanner, NodeJs
Step6A: Install Plugin
Goto Manage Jenkins →Plugins → Available Plugins →
Install below plugins
1 → Eclipse Temurin Installer (Install without restart)
2 → SonarQube Scanner (Install without restart)
3 → NodeJs Plugin (Install Without restart)


Step6B: Configure Java and Nodejs in Global Tool Configuration
Goto Manage Jenkins → Tools → Install JDK(17) and NodeJs(16)→ Click on Apply and Save


Step6C: Configure Sonar Server in Manage Jenkins
Grab the Public IP Address of your EC2 Instance, Sonarqube works on Port 9000, so <Public IP>:9000. Goto your Sonarqube Server. Click on Administration → Security → Users → Click on Tokens and Update Token → Give it a name → and click on Generate Token

click on update Token

Create a token with a name and generate
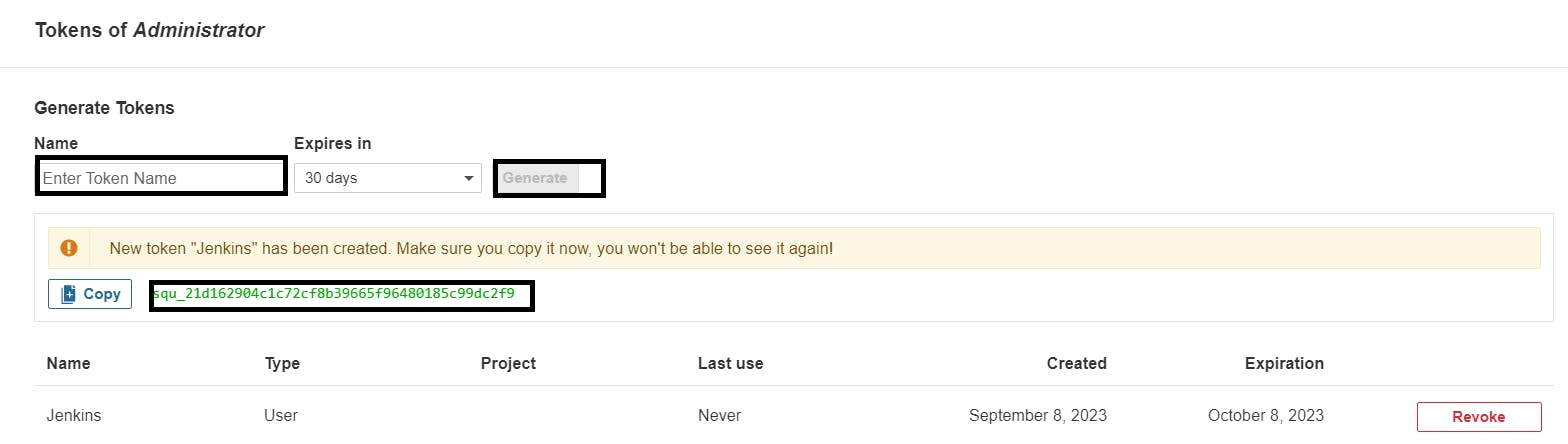
copy Token
Goto Jenkins Dashboard → Manage Jenkins → Credentials → Add Secret Text. It should look like this

You will this page once you click on create

Now, go to Dashboard → Manage Jenkins → System and Add like the below image.

Click on Apply and Save
The Configure System option is used in Jenkins to configure different server
Global Tool Configuration is used to configure different tools that we install using Plugins
We will install a sonar scanner in the tools.

In the Sonarqube Dashboard add a quality gate also
Administration–> Configuration–>Webhooks

Click on Create

Add details
#in url section of quality gate
<http://jenkins-public-ip:8080>/sonarqube-webhook/
Step6D: Add New stages to the pipeline
Go to vs code and create a file sonarqubeAnalysis.groovy & add the below code and push to Jenkins shared library GitHub Repo.
def call() {
withSonarQubeEnv('sonar-server') {
sh ''' $SCANNER_HOME/bin/sonar-scanner -Dsonar.projectName=Youtube -Dsonar.projectKey=Youtube '''
}
}Create another file for qualityGate.groovy
def call(credentialsId) {
waitForQualityGate abortPipeline: false, credentialsId: credentialsId
}Create another file for npmInstall.groovy
def call() {
sh 'npm install'
}Push them to the GitHub Jenkins shared library
git add .
git commit -m "message"
git push origin mainAdd these stages to the pipeline now
#under parameters
tools{
jdk 'jdk17'
nodejs 'node16'
}
environment {
SCANNER_HOME=tool 'sonar-scanner'
}
# add in stages
stage('sonarqube Analysis'){
when { expression { params.action == 'create'}}
steps{
sonarqubeAnalysis()
}
}
stage('sonarqube QualitGate'){
when { expression { params.action == 'create'}}
steps{
script{
def credentialsId = 'Sonar-token'
qualityGate(credentialsId)
}
}
}
stage('Npm'){
when { expression { params.action == 'create'}}
steps{
npmInstall()
}
}Build now.
Stage view

To see the report, you can go to Sonarqube Server and go to Projects.

You can see the report has been generated and the status shows as passed. You can see that there are 517 lines scanned. To see a detailed report, you can go to issues.
Slack Notification

Step7: Install OWASP Dependency Check Plugins
GotoDashboard → Manage Jenkins → Plugins → OWASP Dependency-Check. Click on it and install it without restart.

First, we configured the Plugin and next, we had to configure the Tool
Goto Dashboard → Manage Jenkins → Tools →

Click on Apply and Save here.
Create a file for trivyFs.groovy
def call() {
sh 'trivy fs . > trivyfs.txt'
}Push to GitHub
git add .
git commit -m "message"
git push origin mainAdd the below stages to the Jenkins pipeline
stage('Trivy file scan'){
when { expression { params.action == 'create'}}
steps{
trivyFs()
}
}
stage('OWASP FS SCAN') {
when { expression { params.action == 'create'}}
steps {
dependencyCheck additionalArguments: '--scan ./ --disableYarnAudit --disableNodeAudit', odcInstallation: 'DP-Check'
dependencyCheckPublisher pattern: '**/dependency-check-report.xml'
}
}Stage with the Dependency Check steps cannot be directly used inside a shared library.
The main reason is that pipelines loaded from shared libraries have more restrictive script security by default. So the dependencyCheck and dependencyCheckPublisher steps would fail with rejected signature errors.
Build now
Stage view

You will see that in status, a graph will also be generated and Vulnerabilities.

Step8A: Docker Image Build and Push
We need to install the Docker tool in our system, Goto Dashboard → Manage Plugins → Available plugins → Search for Docker and install these plugins
Docker
Docker Commons
Docker Pipeline
Docker API
docker-build-step
and click on install without restart

Now, goto Dashboard → Manage Jenkins → Tools →
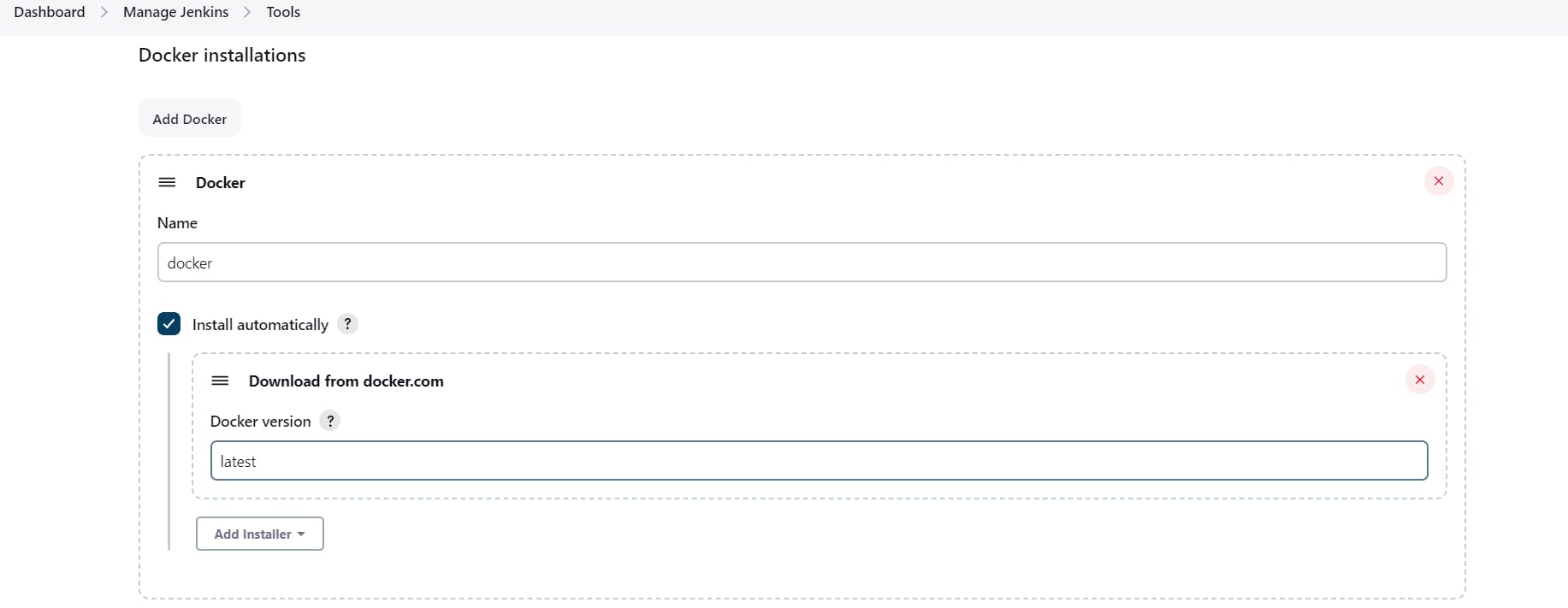
Add DockerHub Username and Password under Global Credentials

Step8B: Create an API key from Rapid API
Open a new tab in the browser and search for rapidapi.com
It will automatically provide your mail and select a mail to create an account

Account is created

Now in the search bar search for YouTube and select YouTube v3

Copy API and use it in the groovy file
docker build –build-arg REACT_APP_RAPID_API_KEY=<API-KEY> -t ${imageName} .

Create a shared library file for dockerBuild.groovy
def call(String dockerHubUsername, String imageName) {
// Build the Docker image
sh "docker build --build-arg REACT_APP_RAPID_API_KEY=f0ead79813mshb0aa -t ${imageName} ."
// Tag the Docker image
sh "docker tag ${imageName} ${dockerHubUsername}/${imageName}:latest"
// Push the Docker image
withDockerRegistry([url: 'https://index.docker.io/v1/', credentialsId: 'docker']) {
sh "docker push ${dockerHubUsername}/${imageName}:latest"
}
}Create another file for trivyImage.groovy
def call() {
sh 'trivy image sevenajay/youtube:latest > trivyimage.txt'
}Push the above files to the GitHub shared library.
git add .
git commit -m "message"
git push origin mainAdd this stage to your pipeline with parameters
#add inside parameter
string(name: 'DOCKER_HUB_USERNAME', defaultValue: 'sevenajay', description: 'Docker Hub Username')
string(name: 'IMAGE_NAME', defaultValue: 'youtube', description: 'Docker Image Name')
#stage
stage('Docker Build'){
when { expression { params.action == 'create'}}
steps{
script{
def dockerHubUsername = params.DOCKER_HUB_USERNAME
def imageName = params.IMAGE_NAME
dockerBuild(dockerHubUsername, imageName)
}
}
}
stage('Trivy iamge'){
when { expression { params.action == 'create'}}
steps{
trivyImage()
}
}Build now with parameters

When you log in to Dockerhub, you will see a new image is created

Step8C: Run the Docker container
Create a new file runContainer.groovy
def call(){
sh "docker run -d --name youtube1 -p 3000:3000 sevenajay/youtube:latest"
}Create Another file to remove container removeContainer.groovy
def call(){
sh 'docker stop youtube1'
sh 'docker rm youtube1'
}Push them to the Shared library GitHub repo
git add .
git commit -m "message"
git push origin mainAdd the below stages to the Pipeline
stage('Run container'){
when { expression { params.action == 'create'}}
steps{
runContainer()
}
}
stage('Remove container'){
when { expression { params.action == 'delete'}}
steps{
removeContainer()
}
}Build with parameters ‘create’

Stage view

It will start the container
<public-ip-jenkins:3000>Output:

Build with parameters ‘delete’

It will stop and remove the Container


Step9A: Kubernetes Setup
Connect your machines to Putty or Mobaxtreme
Take-Two Ubuntu 20.04(t2.medium) instances one for k8s master and the other one for worker.
Install Kubectl on Jenkins machine also.
Step9B: Kubectl is to be installed on Jenkins
Connect your Jenkins machine
Create a shell script file kube.sh
sudo vi kube.shPaste the below commands
sudo apt update
sudo apt install curl -y
curl -LO https://dl.k8s.io/release/$(curl -L -s https://dl.k8s.io/release/stable.txt)/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl
sudo install -o root -g root -m 0755 kubectl /usr/local/bin/kubectl
kubectl version --clientStep9C: K8S Master-Slave setup
Part 1 ———-Master Node————
sudo hostnamectl set-hostname K8s-Master
———-Worker Node————
sudo hostnamectl set-hostname K8s-Worker
Part 2 ————Both Master & Node ————
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install -y docker.io
sudo usermod –aG docker Ubuntu
newgrp docker
sudo chmod 777 /var/run/docker.sock
sudo apt-get update
# apt-transport-https may be a dummy package; if so, you can skip that package
sudo apt-get install -y apt-transport-https ca-certificates curl gpg
curl -fsSL https://pkgs.k8s.io/core:/stable:/v1.29/deb/Release.key | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /etc/apt/keyrings/kubernetes-apt-keyring.gpg
echo 'deb [signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/kubernetes-apt-keyring.gpg] https://pkgs.k8s.io/core:/stable:/v1.29/deb/ /' | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/kubernetes.list
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install -y kubelet kubeadm kubectl
sudo apt-mark hold kubelet kubeadm kubectl sudo snap install kube-apiserverPart 3 ————— Master —————
sudo kubeadm init --pod-network-cidr=10.244.0.0/16
# in case your in root exit from it and run below commands
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/coreos/flannel/master/Documentation/kube-flannel.yml———-Worker Node————
sudo kubeadm join <master-node-ip>:<master-node-port> --token <token> --discovery-token-ca-cert-hash <hash>
Copy the config file to Jenkins master or the local file manager and save it

copy it and save it in documents or another folder save it as secret-file.txt
Note: create a secret-file.txt in your file explorer save the config in it and use this at the kubernetes credential section.
Install Kubernetes Plugin, Once it’s installed successfully

goto manage Jenkins –> manage credentials –> Click on Jenkins global –> add credentials

Step9D: Install Helm & Monitoring K8S using Prometheus and Grafana
On Kubernetes Master install the helm
curl -fsSL -o get_helm.sh https://raw.githubusercontent.com/helm/helm/main/scripts/get-helm-3
chmod 700 get_helm.sh
./get_helm.sh


See the Helm version
helm version --client
We need to add the Helm Stable Charts for your local client. Execute the below command:
helm repo add stable https://charts.helm.sh/stable
Add Prometheus Helm repo
helm repo add prometheus-community https://prometheus-community.github.io/helm-charts
Create Prometheus namespace
kubectl create namespace prometheus
Install kube-Prometheus-stack
Below is the command to install kube-prometheus-stack. The helm repo kube-stack-Prometheus (formerly Prometheus-operator) comes with a Grafana deployment embedded.
helm install stable prometheus-community/kube-prometheus-stack -n prometheus
Let’s check if the Prometheus and Grafana pods are running or not
kubectl get pods -n prometheus
Now See the services
kubectl get svc -n prometheus
This confirms that Prometheus and grafana have been installed successfully using Helm.
To make Prometheus and grafana available outside the cluster, use LoadBalancer or NodePort instead of ClusterIP.
Edit Prometheus Service
kubectl edit svc stable-kube-prometheus-sta-prometheus -n prometheus

Edit Grafana Service
kubectl edit svc stable-grafana -n prometheus

Verify if the service is changed to LoadBalancer and also get the Load BalancerPorts.
kubectl get svc -n prometheus
Access Grafana UI in the browser
Get the external IP from the above screenshot and put it in the browser
<k8s-master-public-ip:external-ip>

Login to Grafana
UserName: admin
Password: prom-operatorCreate a Dashboard in Grafana
In Grafana, we can create various kinds of dashboards as per our needs.
How to Create Kubernetes Monitoring Dashboard?
For creating a dashboard to monitor the cluster:
Click the ‘+’ button on the left panel and select ‘Import’.
Enter the 15661 dashboard id under Grafana.com Dashboard.
Click ‘Load’.

Select ‘Prometheus’ as the endpoint under the Prometheus data sources drop-down.

Click ‘Import’.
This will show the monitoring dashboard for all cluster nodes

How to Create Kubernetes Cluster Monitoring Dashboard?
For creating a dashboard to monitor the cluster:
Click the ‘+’ button on the left panel and select ‘Import’.
Enter 3119 dashboard ID under Grafana.com Dashboard.
Click ‘Load’.
Select ‘Prometheus’ as the endpoint under the Prometheus data sources drop-down.
Click ‘Import’.
This will show the monitoring dashboard for all cluster nodes

Create a POD Monitoring Dashboard
For creating a dashboard to monitor the cluster:
Click the ‘+’ button on the left panel and select ‘Import’.
Enter 6417 dashboard ID under Grafana.com Dashboard.
Click ‘Load’.
Select ‘Prometheus’ as the endpoint under the Prometheus data sources drop-down.
Click ‘Import’.

Step9E: K8S Deployment
Let’s Create a Shared Jenkins library file for K8s deploy and delete
Name kubeDeploy.groovy
def call() {
withKubeConfig(caCertificate: '', clusterName: '', contextName: '', credentialsId: 'k8s', namespace: '', restrictKubeConfigAccess: false, serverUrl: '') {
sh "kubectl apply -f deployment.yml"
}
}To delete deployment
Name kubeDelete.groovy
def call() {
withKubeConfig(caCertificate: '', clusterName: '', contextName: '', credentialsId: 'k8s', namespace: '', restrictKubeConfigAccess: false, serverUrl: '') {
sh "kubectl delete -f deployment.yml"
}
}Let’s push them to GitHub
git add .
git commit -m "message"
git push origin mainThe final stage of the Pipeline
stage('Kube deploy'){
when { expression { params.action == 'create'}}
steps{
kubeDeploy()
}
}
stage('kube deleter'){
when { expression { params.action == 'delete'}}
steps{
kubeDelete()
}
}Build Now with parameters ‘create’
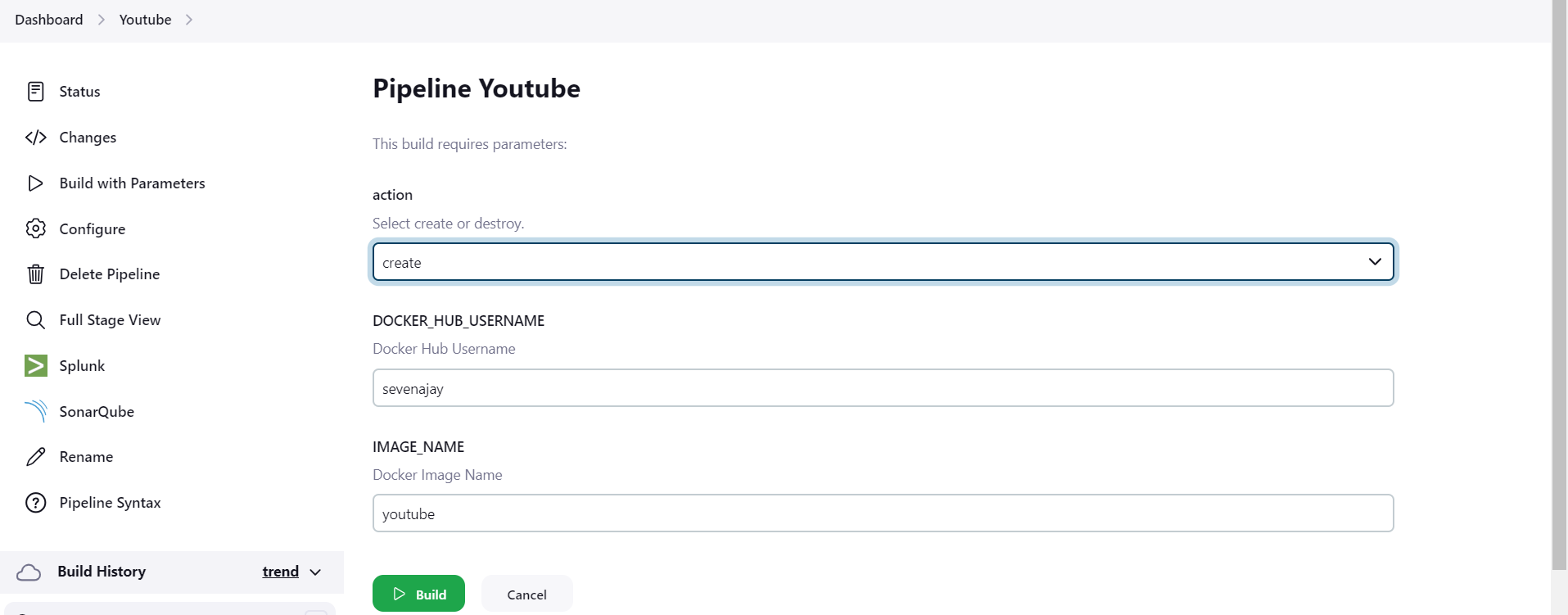
It will apply the deployment
stage view

kubectl get all (or)
kubectl get svc<kubernetes-worker-ip:svc port>
output:



Build with parameter ‘delete’
It will destroy Container and Kubernetes deployment.

Slack Notifications

Splunk


Pipeline
@Library('Jenkins_shared_library') _
def COLOR_MAP = [
'FAILURE' : 'danger',
'SUCCESS' : 'good'
]
pipeline{
agent any
parameters {
choice(name: 'action', choices: 'create\ndelete', description: 'Select create or destroy.')
string(name: 'DOCKER_HUB_USERNAME', defaultValue: 'sevenajay', description: 'Docker Hub Username')
string(name: 'IMAGE_NAME', defaultValue: 'youtube', description: 'Docker Image Name')
}
tools{
jdk 'jdk17'
nodejs 'node16'
}
environment {
SCANNER_HOME=tool 'sonar-scanner'
}
stages{
stage('clean workspace'){
steps{
cleanWorkspace()
}
}
stage('checkout from Git'){
steps{
checkoutGit('https://github.com/Aj7Ay/Youtube-clone-app.git', 'main')
}
}
stage('sonarqube Analysis'){
when { expression { params.action == 'create'}}
steps{
sonarqubeAnalysis()
}
}
stage('sonarqube QualitGate'){
when { expression { params.action == 'create'}}
steps{
script{
def credentialsId = 'Sonar-token'
qualityGate(credentialsId)
}
}
}
stage('Npm'){
when { expression { params.action == 'create'}}
steps{
npmInstall()
}
}
stage('Trivy file scan'){
when { expression { params.action == 'create'}}
steps{
trivyFs()
}
}
stage('OWASP FS SCAN') {
steps {
dependencyCheck additionalArguments: '--scan ./ --disableYarnAudit --disableNodeAudit', odcInstallation: 'DP-Check'
dependencyCheckPublisher pattern: '**/dependency-check-report.xml'
}
}
stage('Docker Build'){
when { expression { params.action == 'create'}}
steps{
script{
def dockerHubUsername = params.DOCKER_HUB_USERNAME
def imageName = params.IMAGE_NAME
dockerBuild(dockerHubUsername, imageName)
}
}
}
stage('Trivy iamge'){
when { expression { params.action == 'create'}}
steps{
trivyImage()
}
}
stage('Run container'){
when { expression { params.action == 'create'}}
steps{
runContainer()
}
}
stage('Remove container'){
when { expression { params.action == 'delete'}}
steps{
removeContainer()
}
}
stage('Kube deploy'){
when { expression { params.action == 'create'}}
steps{
kubeDeploy()
}
}
stage('kube deleter'){
when { expression { params.action == 'delete'}}
steps{
kubeDelete()
}
}
}
post {
always {
echo 'Slack Notifications'
slackSend (
channel: '#channel name', #change your channel name
color: COLOR_MAP[currentBuild.currentResult],
message: "*${currentBuild.currentResult}:* Job ${env.JOB_NAME} \n build ${env.BUILD_NUMBER} \n More info at: ${env.BUILD_URL}"
)
}
}
}In conclusion, deploying a YouTube clone app on Docker and Kubernetes with a strong DevSecOps approach and Jenkins Shared Library is a powerful combination that can take your application deployment to the next level. It provides the security, scalability, and efficiency needed to ensure a smooth transition to production.
By implementing DevSecOps practices from the very beginning and utilizing the orchestration capabilities of Kubernetes, your app will be more secure and ready to handle the demands of your growing user base. Docker containers will give you the flexibility to move your app across different environments with ease, ensuring consistency and reducing deployment-related issues.
Jenkins Shared Library is your key to streamlined, automated, and standardized CI/CD workflows, simplifying the deployment process and making it reproducible and consistent. With these tools and practices in your arsenal, you’ll be well-prepared to face the challenges of modern application deployment.
We hope this tutorial has been valuable in helping you understand the essential components of a DevSecOps-driven deployment. As you embark on your journey to deploy your own YouTube clone app, remember that learning and refining these skills takes time and practice. Don’t be discouraged by challenges; instead, see them as opportunities to grow and improve your expertise.
If you found this tutorial helpful, please share it with your network, and consider subscribing to our blog or channel for more in-depth technical guides. We’re here to support you and answer any questions you may have along the way.
Thank you for joining us on this deployment journey. We wish you the best of luck in your application deployment endeavours. Stay curious, keep learning, and continue to explore the exciting world of DevSecOps, containers, and orchestration!
Here’s to your success in the world of tech and DevSecOps!

Leave a Reply