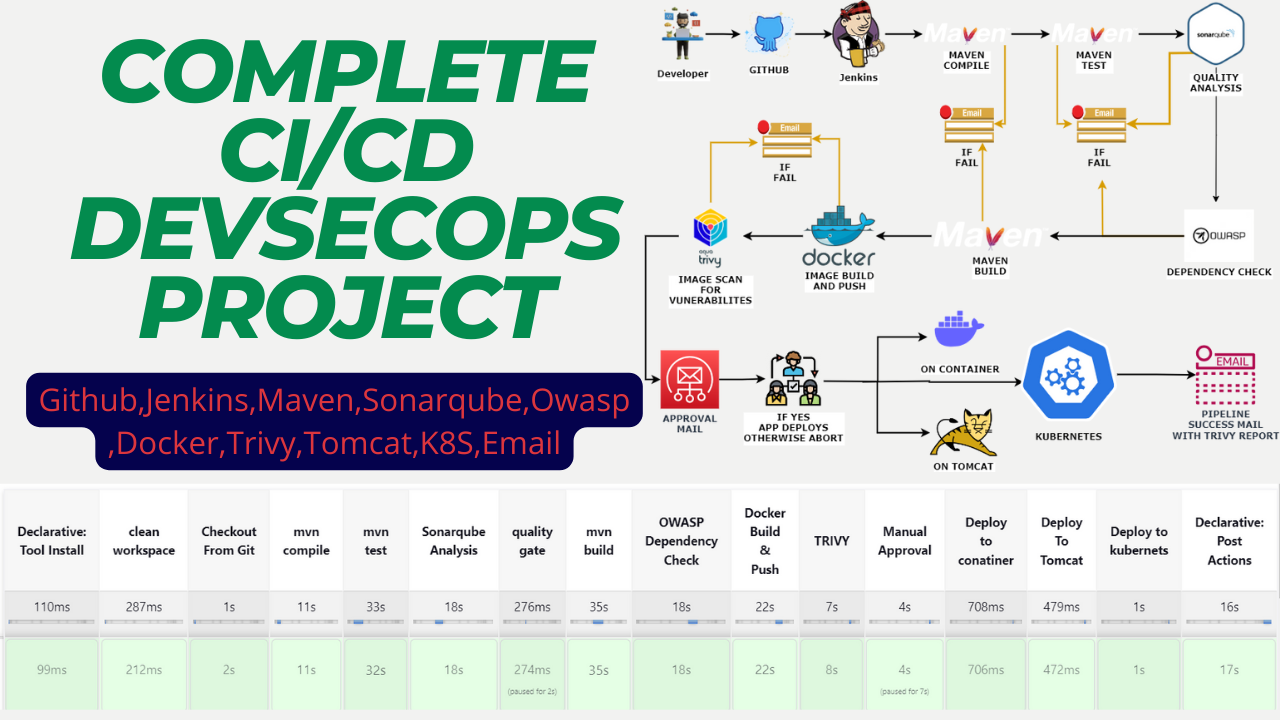
Hello friends, we will be deploying a Pet Clinic Java Based Application. This is an everyday use case scenario used by several organizations. We will be using Jenkins as a CICD tool and deploying our application on Tomcat Server. Hope this detailed blog is useful.
We will be deploying our application in two ways, using Docker Container and other is using Tomcat Server. Finally, we will deploy Kubernetes Also.
And integrates manual approval also in this project.

Steps:-
Step 1 — Create an Ubuntu T2 Large Instance
Step 2 — Install Jenkins, Docker and Trivy. Create a Sonarqube Container using Docker.
Step 3 — Install Plugins like JDK, Sonarqube Scanner, Maven, OWASP Dependency Check,
Step 4 — Create a Pipeline Project in Jenkins using a Declarative Pipeline
Step 5 — Install OWASP Dependency Check Plugins
Step 6 — Docker Image Build and Push
Step 7 — Deploy the image using Docker
Step 8 — Install Tomcat on Port 8083 and finally deploy on Apache Tomcat
Step 9 — Deploy on Kubernetes
Step 10 — Access the Real World Application
Step 11 — Terminate the AWS EC2 Instance
Now, let’s get started and dig deeper into each of these steps:-
Step 1 — Launch an AWS T2 Large Instance. Use the image as Ubuntu. You can create a new key pair or use an existing one. Enable HTTP and HTTPS settings in the Security Group.

Step 2 — Install Jenkins, Docker and Trivy
2A — To Install Jenkins
Connect to your console, and enter these commands to Install Jenkins.
sudo vi jenkins.sh # or use userdata
sudo apt-get update
curl -fsSL https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable/jenkins.io-2023.key | sudo tee \
/usr/share/keyrings/jenkins-keyring.asc > /dev/null
echo deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/jenkins-keyring.asc] \
https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable binary/ | sudo tee \
/etc/apt/sources.list.d/jenkins.list > /dev/null
sudo apt update
sudo apt install openjdk-17-jdk -y
sudo apt install openjdk-17-jre -y
sudo systemctl enable jenkins
sudo systemctl start jenkins
sudo systemctl status jenkins
#save and exit
sudo chmod 777 jenkins.sh
./jenkins.shOnce Jenkins is installed, you will need to go to your AWS EC2 Security Group and open Inbound Port 8080, since Jenkins works on Port 8080.

Now, grab your Public IP Address
EC2 Public IP Address:8080
sudo cat /var/lib/jenkins/secrets/initialAdminPasswordUnlock Jenkins using an administrative password and install the required plugins.

Jenkins will now get installed and install all the libraries.

Jenkins Getting Started Screen

2B — Install Docker
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install docker.io -y
sudo usermod -aG docker $USER
sudo chmod 777 /var/run/docker.sock
sudo docker psAfter the docker installation, we create a sonarqube container (Remember added 9000 port in the security group)

docker run -d --name sonar -p 9000:9000 sonarqube:lts-community

username admin
password admin
2C — Install Trivy
vi trivy.sh
#Enter these
sudo apt-get install wget apt-transport-https gnupg lsb-release -y
wget -qO - https://aquasecurity.github.io/trivy-repo/deb/public.key | gpg --dearmor | sudo tee /usr/share/keyrings/trivy.gpg > /dev/null
echo "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/trivy.gpg] https://aquasecurity.github.io/trivy-repo/deb $(lsb_release -sc) main" | sudo tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list.d/trivy.list
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install trivy -y
#SAVE AND EXIt
sudo chmod 777 trivy.sh
./trivy.shNext, we will log in to Jenkins and start to configure our Pipeline in Jenkins
Step 3 — Install Plugins like JDK, Sonarqube Scanner, Maven, OWASP Dependency Check,
3A — Install Plugin
Goto Manage Jenkins →Plugins → Available Plugins →
Install below plugins
1 → Eclipse Temurin Installer (Install without restart)
2 → SonarQube Scanner (Install without restart)
3B — Configure Java and Maven in Global Tool Configuration
Goto Manage Jenkins → Tools → Install JDK and Maven3 → Click on Apply and Save
3C — Create a Job
Label it as Real-World CI-CD, click on Pipeline and OK.

Enter this in Pipeline Script,
pipeline {
agent any
tools{
jdk 'jdk17'
maven 'maven3'
}
stages{
stage("Git Checkout"){
steps{
git branch: 'main', changelog: false, poll: false, url: 'https://github.com/Aj7Ay/Petclinic.git'
}
}
stage("Compile"){
steps{
sh "mvn clean compile"
}
}
stage("Test Cases"){
steps{
sh "mvn test"
}
}
}
}The stage view would look like this,

Step 4 — Configure Sonar Server in Manage Jenkins
Grab the Public IP Address of your EC2 Instance, Sonarqube works on Port 9000, sp <Public IP>:9000. Goto your Sonarqube Server. Click on Administration → Security → Users → Click on Tokens and Update Token → Give it a name → and click on Generate Token

Click on Update Token

Copy this Token
Goto Dashboard → Manage Jenkins → Credentials → Add Secret Text. It should look like this

Now, go to Dashboard → Manage Jenkins → Configure System

Click on Apply and Save
The Configure System option is used in Jenkins to configure different server
Global Tool Configuration is used to configure different tools that we install using Plugins
We will install a sonar scanner in the tools.

Add Quality Gate in Sonarqube
click on Administration –> Configuration –> webhooks

Click on Create

Enter a URL like the below image

Let go to our Pipeline and add the Sonar-qube Stage in our Pipeline Script
stage("Sonarqube Analysis "){
steps{
withSonarQubeEnv('sonar-server') {
sh ''' $SCANNER_HOME/bin/sonar-scanner -Dsonar.projectName=Petclinic \
-Dsonar.java.binaries=. \
-Dsonar.projectKey=Petclinic '''
}
}
}
steps {
steps {
waitForQualityGate abortPipeline: false, credentialsId: 'Sonar-token'
}
}
#alternative Sonarqube Analysis
stage ('sonarqube Analysis'){
steps{
script{
withSonarQubeEnv(credentialsId: 'Sonar-token') {
sh 'mvn sonar:sonar'
}
}
}
}Click on Build now, you will see the stage view like this

To see the report, you can go to Sonarqube Server and go to Projects.

You can see the report has been generated and the status shows as passed. You can see that there are 15K lines. To see a detailed report, you can go to issues.
Step 5 — Install OWASP Dependency Check Plugins
GotoDashboard → Manage Jenkins → Plugins → OWASP Dependency-Check. Click on it and install it without restarting.

First, we configured the Plugin and next, we had to configure the Tool
Goto Dashboard → Manage Jenkins → Tools →

Click on Apply and Save here.
Now go configure → Pipeline and add this stage to your pipeline
stage('OWASP FS SCAN') {
steps {
dependencyCheck additionalArguments: '--scan ./ --disableYarnAudit --disableNodeAudit', odcInstallation: 'DP-Check'
dependencyCheckPublisher pattern: '**/dependency-check-report.xml'
}
}The final pipeline would look like this,
pipeline {
agent any
tools{
jdk 'jdk17'
maven 'maven3'
}
environment {
SCANNER_HOME=tool 'sonar-scanner'
}
stages{
stage("Git Checkout"){
steps{
git branch: 'main', changelog: false, poll: false, url: 'https://github.com/Aj7Ay/Petclinic.git'
}
}
stage("Compile"){
steps{
sh "mvn clean compile"
}
}
stage("Test Cases"){
steps{
sh "mvn test"
}
}
stage("Sonarqube Analysis "){
steps{
withSonarQubeEnv('sonar-server') {
sh ''' $SCANNER_HOME/bin/sonar-scanner -Dsonar.projectName=Petclinic \
-Dsonar.java.binaries=. \
-Dsonar.projectKey=Petclinic '''
}
}
}
stage("Build"){
steps{
sh " mvn clean install"
}
}The stage view would look like this,

You will see that in status, a graph will also be generated

Step 6 — Docker Image Build and Push
We need to install the Docker tool in our system, Goto Dashboard → Manage Plugins → Available plugins → Search for Docker and install these plugins
Docker
Docker Commons
Docker Pipeline
Docker API
docker-build-step
and click on install without restart
Now, goto Dashboard → Manage Jenkins → Tools →

Add DockerHub Username and Password under Global Credentials

Add this stage to Pipeline Script
stage("Docker Build & Push"){
steps{
script{
withDockerRegistry(credentialsId: ‘docker', toolName: 'docker') {
sh "docker build -t petclinic1 ."
sh "docker tag petclinic1 Aj7Ay/pet-clinic123:latest "
sh "docker push Aj7Ay/pet-clinic123:latest "
}
}
}
}You will see the output below,

Now, when you do
You will see this output

When you log in to Dockerhub, you will see a new image is created
Step 7 — Deploy the image using Docker
Add this stage to your pipeline syntax
stage("Deploy Using Docker"){
steps{
sh " docker run -d --name pet1 -p 8082:8082 Aj7Ay/pet-clinic123:latest "
}
}You will see the Stage View like this,

Step 8 — Install Tomcat on Port 8083 and finally deploy on Apache Tomcat
Before we add Pipeline Script, we need to install and configure Tomcat on our server.
Here are the steps to install Tomcat 9
Change to opt directory
cd /optDownload the Tomcat file using the wget command
sudo wget https://archive.apache.org/dist/tomcat/tomcat-9/v9.0.65/bin/apache-tomcat-9.0.65.tar.gz
sudo wget https://dlcdn.apache.org/tomcat/tomcat-9/v9.0.80/bin/apache-tomcat-9.0.80.tar.gz (Another link )Unzip tar file
sudo tar -xvf apache-tomcat-9.0.65.tar.gzMove to the conf directory and change the port in the Tomcat server to another port from the default port
cd /opt/apache-tomcat-9.0.65/conf
vi server.xmlUpdate Tomcat users’ XML file for manager app login
cd /opt/apache-tomcat-9.0.65/conf
sudo vi tomcat-users.xml—add-below-line at the end (2nd-last line)—-
<user username="admin" password="admin1234" roles="admin-gui, manager-gui"/>Create a symbolic link for the direct start and stop of Tomcat
sudo ln -s /opt/apache-tomcat-9.0.65/bin/startup.sh /usr/bin/startTomcat
sudo ln -s /opt/apache-tomcat-9.0.65/bin/shutdown.sh /usr/bin/stopTomcatGo to this path and comment below lines in manager and host-manager
sudo vi /opt/apache-tomcat-9.0.65/webapps/manager/META-INF/context.xml
#comment these lines
<!-- Valve className="org.apache.catalina.valves.RemoteAddrValve"
allow="127\.\d+\.\d+\.\d+|::1|0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1" /> -->sudo vi /opt/apache-tomcat-9.0.65/webapps/host-manager/META-INF/context.xml
#comment these lines
<!-- Valve className="org.apache.catalina.valves.RemoteAddrValve"
allow="127\.\d+\.\d+\.\d+|::1|0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1" /> -->sudo stopTomcat
sudo startTomcatCertainly! To allow both ubuntu and Jenkins users to copy the petclinic.war file to the /opt/apache-tomcat-9.0.65/webapps/ directory without entering passwords, you can add the appropriate entries to the /etc/sudoers file. Here’s how you can do it:
Open a terminal.
Use the sudo command to edit the sudoers file using a text editor like visudo:
sudo visudoScroll down to an appropriate section (e.g., just below the line with %sudo ALL=(ALL:ALL) ALL) and add the following lines:
#after workspace change your job name
ubuntu ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: /bin/cp /var/lib/jenkins/workspace/petclinic/target/petclinic.war /opt/apache-tomcat-9.0.65/webapps/
jenkins ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: /bin/cp /var/lib/jenkins/workspace/petclinic/target/petclinic.war /opt/apache-tomcat-9.0.65/webapps/Save the file and exit the text editor.
By adding these lines, you’re allowing both the Ubuntu user and the Jenkins user to run the specified cp command without being prompted for a password.
After making these changes, both users should be able to run the Jenkins job that copies the petclinic.war file to the specified directory without encountering permission issues. Always ensure that you’re cautious when editing the sudoers file and that you verify the paths and syntax before saving any changes.
Since 8080 is being used by Jenkins, we have used Port 8083 to host the Tomcat Server

Add this stage to your Pipeline script
stage("Deploy To Tomcat"){
steps{
sh "cp /var/lib/jenkins/workspace/Real-World-CI-CD/target/petclinic.war /opt/apache-tomcat-9.0.65/webapps/ "
}
}Kindly note that this application can be deployed via Docker and also via Tomcat Server. Here I have used Tomcat to deploy the application
The final script looks like this(Rough),
#rough pipeline just for reference complete pipeline at end
pipeline {
agent any
tools{
jdk 'jdk17'
maven 'maven3'
}
environment {
SCANNER_HOME=tool 'sonar-scanner'
}
stages{
stage("Git Checkout"){
steps{
git branch: 'main', changelog: false, poll: false, url: 'https://github.com/Aj7Ay/Petclinic.git'
}
}
stage("Compile"){
steps{
sh "mvn clean compile"
}
}
stage("Test Cases"){
steps{
sh "mvn test"
}
}
stage("Build"){
steps{
sh " mvn clean install"
}
}
stage("OWASP Dependency Check"){
steps{
dependencyCheck additionalArguments: '--scan ./ --format XML ' , odcInstallation: 'DP-Check'
dependencyCheckPublisher pattern: '**/dependency-check-report.xml'
}
}
stage("Docker Build & Push"){
steps{
script{
withDockerRegistry(credentialsId: 'docker’, toolName: 'docker') {
sh "docker build -t petclinic1 ."
sh "docker tag petclinic1 Aj7Ay/pet-clinic123:latest "
sh "docker push Aj7Ay/pet-clinic123:latest "
}
}
}
}
stage("Deploy Using Docker"){
steps{
sh " docker run -d --name pet12 -p 8082:8082 Aj7Ay/pet-clinic123:latest "
}
}
stage("Deploy To Tomcat"){
steps{
sh "cp target/petclinic.war /opt/apache-tomcat-9.0.65/webapps/ "
}
}
}
}And you can access your application on Port 8083. This is a Real World Application that has all Functional Tabs.

Step 9 — Access the Real World Application
public-ip:8083/petclinic
STEP:10 Take Two Ubuntu 20.04 instances one for the k8s master and the other one for the worker Also install on the Jenkins machine (only kubectl)
Kubectl on Jenkins to be installed
sudo apt update
sudo apt install curl
curl -LO https://dl.k8s.io/release/$(curl -L -s https://dl.k8s.io/release/stable.txt)/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl
sudo install -o root -g root -m 0755 kubectl /usr/local/bin/kubectl
kubectl version –clientPart 1 ————-Master ————
sudo su
hostname master
bash
clear————-Node ————–
sudo su
hostname worker
bash
clearPart 2 ——————-Both Master & Node ————-
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install -y docker.io
sudo usermod –aG docker Ubuntu
newgrp docker
sudo chmod 777 /var/run/docker.sock
sudo curl -s https://packages.cloud.google.com/apt/doc/apt-key.gpg | sudo apt-key add -
sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/kubernetes.list <<EOF
deb https://apt.kubernetes.io/ kubernetes-xenial main
EOF
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install -y kubelet kubeadm kubectl
sudo snap install kube-apiserverPart 3 ——————–Master —————
sudo kubeadm init --pod-network-cidr=10.244.0.0/16
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/coreos/flannel/master/Documentation/kube-flannel.yml————-Node ———-
#paste the kube adm join command which is in this format:
sudo kubeadm join <master-node-ip>:<master-node-port> --token <token> --discovery-token-ca-cert-hash <hash>on Master
kubectl get nodesCONGRATULATIONS ON YOUR NEW KUBERNETES CLUSTER ON UBUNTU ON EC2
Copy the config file to Jenkins master or the local file manager and save it
Install Kubernetes plugins
Install the Kubernetes Plugin, once it’s installed successfully. Go to manage Jenkins –> manage credentials –> Click on Jenkins global –> add credentials.
Configuring mail server in Jenkins ( Gmail )
Install Email Extension Plugin in Jenkins
Once the plugin is installed in Jenkins, click on manage Jenkins –> configure system there under the E-mail Notification section configure the details as shown in the below image

This is to just verify the mail configuration
Now under the Extended E-mail Notification section configure the details as shown in the below images



By using the below code I can send customized mail.
post {
always {
emailext attachLog: true,
subject: "'${currentBuild.result}'",
body: "Project: ${env.JOB_NAME}<br/>" +
"Build Number: ${env.BUILD_NUMBER}<br/>" +
"URL: ${env.BUILD_URL}<br/>",
to: 'postbox.aj99@gmail.com', #change mail here
attachmentsPattern: 'trivy.txt'
}
}Add Kubernetes deployment to Pipeline.
stage('Deploy to kubernets'){
steps{
script{
withKubeConfig(caCertificate: '', clusterName: '', contextName: '', credentialsId: 'k8s', namespace: '', restrictKubeConfigAccess: false, serverUrl: '') {
sh 'kubectl apply -f deployment.yaml'
}
}
}#after deployment in kubernetes cluster enter this command
kubectl get all # to check everything is deployed or notStep 11 — Terminate the AWS EC2 Instance
Lastly, do not forget to terminate the AWS EC2 Instance.
Complete Pipeline
pipeline{
agent any
tools{
jdk 'jdk17'
maven 'maven3'
}
environment {
SCANNER_HOME=tool 'sonar-scanner'
}
stages {
stage('clean workspace'){
steps{
cleanWs()
}
}
stage('Checkout From Git'){
steps{
git branch: 'main', url: 'https://github.com/Aj7Ay/Petclinic-Real.git'
}
}
stage('mvn compile'){
steps{
sh 'mvn clean compile'
}
}
stage('mvn test'){
steps{
sh 'mvn test'
}
}
stage("Sonarqube Analysis "){
steps{
withSonarQubeEnv('sonar-server') {
sh ''' $SCANNER_HOME/bin/sonar-scanner -Dsonar.projectName=Petclinic \
-Dsonar.java.binaries=. \
-Dsonar.projectKey=Petclinic '''
}
}
}
stage("quality gate"){
steps {
script {
waitForQualityGate abortPipeline: false, credentialsId: 'Sonar-token'
}
}
}
stage('mvn build'){
steps{
sh 'mvn clean install'
}
}
stage("OWASP Dependency Check"){
steps{
dependencyCheck additionalArguments: '--scan ./ --format HTML ', odcInstallation: 'DP-Check'
dependencyCheckPublisher pattern: '**/dependency-check-report.html'
}
}
stage("Docker Build & Push"){
steps{
script{
withDockerRegistry(credentialsId: 'docker', toolName: 'docker'){
sh "docker build -t petclinic1 ."
sh "docker tag petclinic1 sevenajay/petclinic1:latest "
sh "docker push sevenajay/petclinic1:latest "
}
}
}
}
stage("TRIVY"){
steps{
sh "trivy image sevenajay/petclinic1:latest > trivy.txt"
}
}
stage('Clean up containers') { //if container runs it will stop and remove this block
steps {
script {
try {
sh 'docker stop pet1'
sh 'docker rm pet1'
} catch (Exception e) {
echo "Container pet1 not found, moving to next stage"
}
}
}
}
stage ('Manual Approval'){
steps {
script {
timeout(time: 10, unit: 'MINUTES') {
def approvalMailContent = """
Project: ${env.JOB_NAME}
Build Number: ${env.BUILD_NUMBER}
Go to build URL and approve the deployment request.
URL de build: ${env.BUILD_URL}
"""
mail(
to: 'postbox.aj99@gmail.com',
subject: "${currentBuild.result} CI: Project name -> ${env.JOB_NAME}",
body: approvalMailContent,
mimeType: 'text/plain'
)
input(
id: "DeployGate",
message: "Deploy ${params.project_name}?",
submitter: "approver",
parameters: [choice(name: 'action', choices: ['Deploy'], description: 'Approve deployment')]
)
}
}
}
}
stage('Deploy to conatiner'){
steps{
sh 'docker run -d --name pet1 -p 8082:8080 sevenajay/petclinic1:latest'
}
}
stage("Deploy To Tomcat"){
steps{
sh "sudo cp /var/lib/jenkins/workspace/petclinic/target/petclinic.war /opt/apache-tomcat-9.0.65/webapps/ "
}
}
stage('Deploy to kubernets'){
steps{
script{
withKubeConfig(caCertificate: '', clusterName: '', contextName: '', credentialsId: 'k8s', namespace: '', restrictKubeConfigAccess: false, serverUrl: '') {
sh 'kubectl apply -f deployment.yaml'
}
}
}
}
}
post {
always {
emailext attachLog: true,
subject: "'${currentBuild.result}'",
body: "Project: ${env.JOB_NAME}<br/>" +
"Build Number: ${env.BUILD_NUMBER}<br/>" +
"URL: ${env.BUILD_URL}<br/>",
to: 'postbox.aj99@gmail.com', #//change mail
attachmentsPattern: 'trivy.txt'
}
}
}
#// try this approval stage also
stage('Manual Approval') {
timeout(time: 10, unit: 'MINUTES') {
mail to: 'postbox.aj99@gmail.com',
subject: "${currentBuild.result} CI: ${env.JOB_NAME}",
body: "Project: ${env.JOB_NAME}\nBuild Number: ${env.BUILD_NUMBER}\nGo to ${env.BUILD_URL} and approve deployment"
input message: "Deploy ${params.project_name}?",
id: "DeployGate",
submitter: "approver",
parameters: [choice(name: 'action', choices: ['Deploy'], description: 'Approve deployment')]
}
}
Leave a Reply