Welcome to our in-depth guide on deploying an Amazon app with a strong focus on security through a DevSecOps approach. In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, building and deploying applications not only requires speed but also airtight security. That’s where DevSecOps comes into play, blending development, security, and operations into a single, unified process. In this blog post, we will embark on a journey where we’ll leverage Terraform, Jenkins CI/CD, SonarQube, and Trivy to create a robust and secure pipeline for deploying applications on Amazon Web Services (AWS). Whether you’re an experienced developer looking to enhance your DevSecOps skills or a newcomer eager to explore this exciting intersection of software development and security, this guide has something valuable to offer. Let’s dive in and explore the steps to safeguard your Amazon app while ensuring smooth and efficient deployment.
COMPLETE PROJECT VIDEO ON YOUTUBE
If you have doubts watch this video on YouTube
https://github.com/Aj7Ay/Amazon-FE.git

Step1: create an IAM user
Navigate to the AWS console
Click the “Search” field.

Search for IAM

Click “Users”

Click “Add users”

Click the “User name” field.

Type “Terraform” or as you wish about the name
Click Next

Click “Attach policies directly”

Click this checkbox with Administrator access

Click “Next”

Click “Create user”

Click newly created user in my case Ajay

Click “Security credentials”

Click “Create access key”

Click this radio button with the CLI

Agree to terms

Click Next

Click “Create access key”

Download .csv file

Step2: Aws Configure
Go to vs code or Cmd your wish
aws configureProvide your Aws Access key and Secret Access key

Step3: Terraform files and Provision Jenkins,sonar
resource "aws_instance" "web" {
ami = "ami-0f5ee92e2d63afc18" #change ami id for different region
instance_type = "t2.large"
key_name = "Mumbai"
vpc_security_group_ids = [aws_security_group.Jenkins-sg.id]
user_data = templatefile("./install.sh", {})
tags = {
Name = "Jenkins-sonarqube"
}
root_block_device {
volume_size = 30
}
}
resource "aws_security_group" "Jenkins-sg" {
name = "Jenkins-sg"
description = "Allow TLS inbound traffic"
ingress = [
for port in [22, 80, 443, 8080, 9000, 3000] : {
description = "inbound rules"
from_port = port
to_port = port
protocol = "tcp"
cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"]
ipv6_cidr_blocks = []
prefix_list_ids = []
security_groups = []
self = false
}
]
egress {
from_port = 0
to_port = 0
protocol = "-1"
cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"]
}
tags = {
Name = "jenkins-sg"
}
}terraform {
required_providers {
aws = {
source = "hashicorp/aws"
version = "~> 5.0"
}
}
}
# Configure the AWS Provider
provider "aws" {
region = "ap-south-1" #change your region
}This will install Jenkins and Docker and Sonarqube and trivy
#!/bin/bash
sudo apt update -y
wget -O - https://packages.adoptium.net/artifactory/api/gpg/key/public | tee /etc/apt/keyrings/adoptium.asc
echo "deb [signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/adoptium.asc] https://packages.adoptium.net/artifactory/deb $(awk -F= '/^VERSION_CODENAME/{print$2}' /etc/os-release) main" | tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/adoptium.list
sudo apt update -y
sudo apt install temurin-17-jdk -y
/usr/bin/java --version
curl -fsSL https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable/jenkins.io-2023.key | sudo tee /usr/share/keyrings/jenkins-keyring.asc > /dev/null
echo deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/jenkins-keyring.asc] https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable binary/ | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/jenkins.list > /dev/null
sudo apt-get update -y
sudo apt-get install jenkins -y
sudo systemctl start jenkins
sudo systemctl status jenkins
#install docker
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install docker.io -y
sudo usermod -aG docker ubuntu
newgrp docker
sudo chmod 777 /var/run/docker.sock
docker run -d --name sonar -p 9000:9000 sonarqube:lts-community
#install trivy
sudo apt-get install wget apt-transport-https gnupg lsb-release -y
wget -qO - https://aquasecurity.github.io/trivy-repo/deb/public.key | gpg --dearmor | sudo tee /usr/share/keyrings/trivy.gpg > /dev/null
echo "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/trivy.gpg] https://aquasecurity.github.io/trivy-repo/deb $(lsb_release -sc) main" | sudo tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list.d/trivy.list
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install trivy -y
Terraform commands to provision
terraform init
terraform validate
terraform plan
terraform apply
output
<instance-ip:8080> #jenkins
sudo cat /var/lib/jenkins/secrets/initialAdminPasswordUnlock Jenkins using an administrative password and install the suggested plugins.
Jenkins will now get installed and install all the libraries.

Create a user click on save and continue.
Jenkins Getting Started Screen.

Copy your Public key again and paste it into a new tab
<instance-public-ip:9000>Now our sonarqube is up and running

Enter username and password, click on login and change password
username admin
password admin
Update New password, This is Sonar Dashboard.

Check trivy version
trivy --versionStep 4 — Install Plugins like JDK, Sonarqube Scanner, NodeJs, OWASP Dependency Check
4A — Install Plugin
Goto Manage Jenkins →Plugins → Available Plugins →
Install below plugins
1 → Eclipse Temurin Installer (Install without restart)
2 → SonarQube Scanner (Install without restart)
3 → NodeJs Plugin (Install Without restart)


4B — Configure Java and Nodejs in Global Tool Configuration
Goto Manage Jenkins → Tools → Install JDK(17) and NodeJs(16)→ Click on Apply and Save


Step 5 — Configure Sonar Server in Manage Jenkins
Grab the Public IP Address of your EC2 Instance, Sonarqube works on Port 9000, so <Public IP>:9000. Goto your Sonarqube Server. Click on Administration → Security → Users → Click on Tokens and Update Token → Give it a name → and click on Generate Token

click on update Token

Create a token with a name and generate
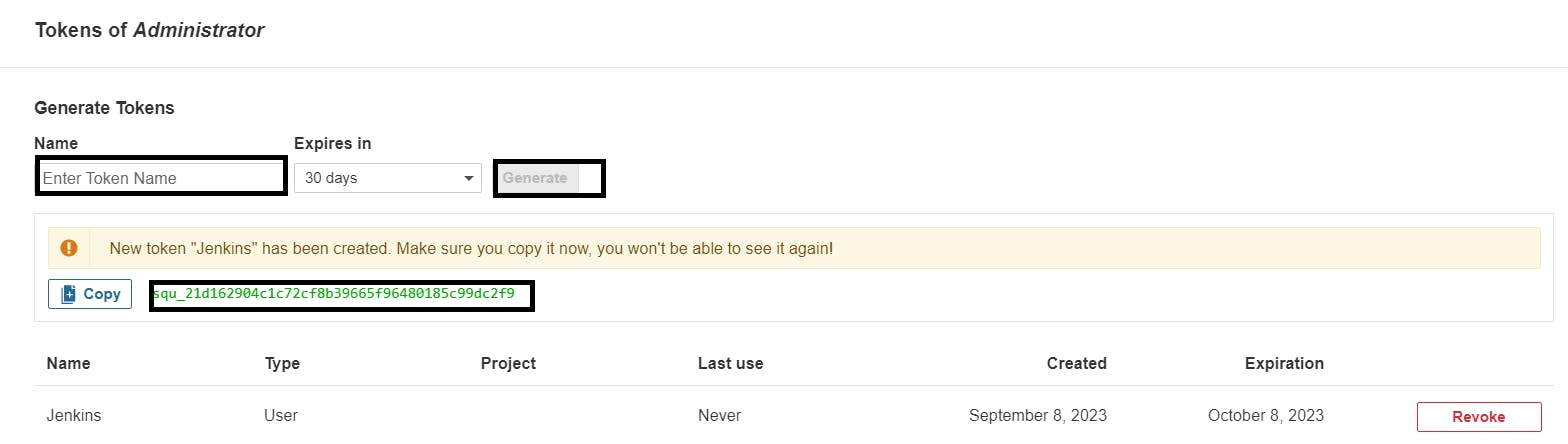
copy Token
Goto Jenkins Dashboard → Manage Jenkins → Credentials → Add Secret Text. It should look like this

You will this page once you click on create

Now, go to Dashboard → Manage Jenkins → System and Add like the below image.

Click on Apply and Save
The Configure System option is used in Jenkins to configure different server
Global Tool Configuration is used to configure different tools that we install using Plugins
We will install a sonar scanner in the tools.

In the Sonarqube Dashboard add a quality gate also
Administration–> Configuration–>Webhooks

Click on Create

Add details
#in url section of quality gate
<http://jenkins-public-ip:8080>/sonarqube-webhook/
Let’s go to our Pipeline and add the script in our Pipeline Script.
pipeline{
agent any
tools{
jdk 'jdk17'
nodejs 'node16'
}
environment {
SCANNER_HOME=tool 'sonar-scanner'
}
stages {
stage('clean workspace'){
steps{
cleanWs()
}
}
stage('Checkout from Git'){
steps{
git branch: 'main', url: 'https://github.com/Aj7Ay/Amazon-FE.git'
}
}
stage("Sonarqube Analysis "){
steps{
withSonarQubeEnv('sonar-server') {
sh ''' $SCANNER_HOME/bin/sonar-scanner -Dsonar.projectName=Amazon \
-Dsonar.projectKey=Amazon '''
}
}
}
stage("quality gate"){
steps {
script {
waitForQualityGate abortPipeline: false, credentialsId: 'Sonar-token'
}
}
}
stage('Install Dependencies') {
steps {
sh "npm install"
}
}
}
}Click on Build now, you will see the stage view like this

To see the report, you can go to Sonarqube Server and go to Projects.

You can see the report has been generated and the status shows as passed. You can see that there are 1k lines it scanned. To see a detailed report, you can go to issues.
Step 6 — Install OWASP Dependency Check Plugins
GotoDashboard → Manage Jenkins → Plugins → OWASP Dependency-Check. Click on it and install it without restart.

First, we configured the Plugin and next, we had to configure the Tool
Goto Dashboard → Manage Jenkins → Tools →

Click on Apply and Save here.
Now go configure → Pipeline and add this stage to your pipeline and build.
stage('OWASP FS SCAN') {
steps {
dependencyCheck additionalArguments: '--scan ./ --disableYarnAudit --disableNodeAudit', odcInstallation: 'DP-Check'
dependencyCheckPublisher pattern: '**/dependency-check-report.xml'
}
}
stage('TRIVY FS SCAN') {
steps {
sh "trivy fs . > trivyfs.txt"
}
}The stage view would look like this,

You will see that in status, a graph will also be generated and Vulnerabilities.

Step 7 — Docker Image Build and Push
We need to install the Docker tool in our system, Goto Dashboard → Manage Plugins → Available plugins → Search for Docker and install these plugins
Docker
Docker Commons
Docker Pipeline
Docker API
docker-build-step
and click on install without restart

Now, goto Dashboard → Manage Jenkins → Tools →
Add DockerHub Username and Password under Global Credentials

Add this stage to Pipeline Script
stage("Docker Build & Push"){
steps{
script{
withDockerRegistry(credentialsId: 'docker', toolName: 'docker'){
sh "docker build -t amazon ."
sh "docker tag amazon sevenajay/amazon:latest "
sh "docker push sevenajay/amazon:latest "
}
}
}
}
stage("TRIVY"){
steps{
sh "trivy image sevenajay/amazon:latest > trivyimage.txt"
}
}You will see the output below, with a dependency trend.

When you log in to Dockerhub, you will see a new image is created

Now Run the container to see if the game coming up or not by adding the below stage
stage('Deploy to container'){
steps{
sh 'docker run -d --name amazon -p 3000:3000 sevenajay/amazon:latest'
}
}stage view

<Jenkins-public-ip:3000>
You will get this output

Let’s destroy everything
Go to VS Code and provide the below command (or) Go to the path where you provisioned the Ec2 instance
terraform destroy --auto-approve
In this age of digital transformation, safeguarding your applications is no longer an option but a necessity. The synergy of Terraform, Jenkins, SonarQube, and Trivy empowers us to not only deploy our applications with speed and efficiency but also to do so with an unwavering focus on security. We hope this guide has been a valuable resource in your journey towards embracing DevSecOps principles and securing your Amazon app deployments on AWS. Remember, the world of technology is ever-evolving, and so are the threats that come with it. Stay vigilant, stay informed, and continue to adapt your DevSecOps practices to stay ahead in the realm of secure and efficient application development. Thank you for joining us, and we wish you every success in your DevSecOps endeavours.

Leave a Reply